RETAIL TRADE
Retail Trade
Meaning of Retail Trade
Define Retail Trade
Retail trade is the sale of goods in small quantities to consumers. OR is a business activity involving buying goods and retailing them to ultimate consumers without changing the physical and chemical form of goods.
Retailer: One who sells goods or commodities directly to consumers. These items are purchased from the manufacturer or wholesaler and sold to the end user at a marked up price. Examples: retailer would be the small family-operated pharmacy on the corner etc.
Difference between Retailing and the Retailer
Distinguish between retailing and the Retailer
RETAILER AND RETAILING.
Retailer is a trader who goods and service to end users. Retailing is the strategies adopted by retailers. in most cases both are same meaning He has a limited sphere in the market.
The Functions of Retail Trade
Point out the functions of retail Trade
Functions
Retailers perform a number of functions. These are:
- The retailer buys a variety of products from the wholesaler or a number of wholesalers. He thus performs two functions like buying of goods and assembling of goods.
- The retailer performs storing function by stocking the goods for a consumer.
- He develops personal contact with the consumers and gives them goods on credit.
- He bears the risks in connection with Physical Spoilage of goods and fall in price. Besides he bears risks on account of fire, theft, deterioration in the quality and spoilage of goods.
- He resorts to standardization and grading of goods in such a way that these are accepted by the customers.
- He makes arrangement for delivery of goods and supply valuable market information to both wholesaler and the consumer.
Service of a Retailer
A retailer provides a number of services to the customer and to the wholesaler.
To Customers:
- He provides ready stock of goods and as such he sells and quantity of goods desired by the customers.
- He keeps a large variety of goods produced by different producers and thereby ensures a wide variety of choice to the customers.
- He relives the consumers of maintaining large quantity of goods for future period because he himself holds large stock of goods.
- He develops personal relationship with the customers by giving them credit.
- he provides free-home delivery service to the customers.
- He informs the new product to the customers.
- he makes arrangement for replacement of goods when he receive complaints.
To Wholesaler:
- He gives valuable market information with regard to taste, fashion and demand for the goods to the wholesaler.
- The retailer maintains direct contact with the customers and so he relieves the wholesaler with regard to maintenance of direct contact.
- He helps the wholesaler in getting their goods distributed to the consumer.
- He is regarded as an important link between the wholesaler and the consumer.
- He creates demand for the products by displaying the goods to the consumers.
Different Types of Retailers
Identify the different types of retailers
TYPES OF RETAIL TRADE
- Small scale retail trade
- large scale trade
Small – scale retailing
Features of Small – scale retailing <!-- [if !supportLineBreakNewLine]--> <!--[endif]-->
- They normally run as a sole proprietorship (sole trader) or a partnership 2.
- The capital is usually small and it is raised from personal saving, borrowed from friends or family or loan from banks 3.
- Small retailers obtain a great variety of goods in small quantities from wholesaler 4.
- The sole proprietorship (sole trader) normally serves his customers with the help of some assistants. Therefore, he has the opportunity to get know his regular customers well
Reasons why Small retailers buy from the Wholesaler <!-- [if !supportLineBreakNewLine]--> <!--[endif]-->
- Small Capital; The small retailer has only a small capital and cannot afford to buy in bulk from the manufacturer therefore he can only make small orders at a particular time
- Limited market; The small retailers has mainly a regular customers therefore the markets is only limited to the people living in the area near their shop
- Small turnover; The total sales per month is small If they buy in bulk, the goods will be laying around and have to pay the rental for storing the goods Furthermore they can go bad in the case of foodstuff or may go out of fashion in the case of goods like clothing and furniture That why they only needs to pay in small amounts for a great variety of goods produced by the manufacturers This is exactly what the wholesaler does for them.
- Need for credit; Trade credit is one of the greatest sources of funds for a small retailer Manufactures are often unwilling to give credit but the wholesalers are willing to give trade to small retailer in order to secure business
- Variety of goods; A wholesaler stocks a great variety of brands of a particulars goods like Lux, Palmolive, Imperial Leather Soap.And they also stocks a wide range of related goods, for example, foodstuff and household items. Retail Traders can be classified into two categories viz; the Itinerant retailers and the Fixed retailers.The Fixed retailers are further subdivided into (a) Small scale and (b) Large scale fixed shop retailers.
The classification of retailers is shown in the following chart:
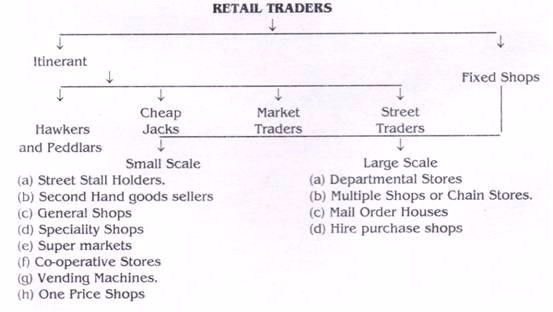
1. Itinerant Retailers:
These retailers do not have the fixed places to carry their trade and generally move from one place to another in order to sell goods. They can be usually seen along the road sides, streets, railway compartments, bus stands, and fairs etc.
They usually possess that stock which can be conveniently sold during the day. They need limited funds to carry their business. These types of retailers deal in daily need articles like vegetables, fruits, milk, eggs and fishes etc.
A brief explanation of this type of retailers is given as under:
- Hawkers and peddlars:These are the petty retailers who carry their products on their heads or on wheeled vehicles from door to door. They usually sell seasonal goods like fruits, vegetables and eatables and also sell certain other goods like pens, toys and utensils, etc.
- Cheap jacks:They hire shops in different residential localities wherein they display their products for sale. They do not stick to one place; rather keep moving from one locality to another. They usually deal in household articles.
- Market traders:They sell their products at periodical markets on ‘market days’. The markets may be weekly or fortnightly. They also sell their wares at different fairs and gatherings.
- Street Traders:These traders are found on the pavements of crowded streets or markets of the cities. They are also known as “pavement retailers” In big cities like Calcutta, Delhi, Mumbai and Chennai etc., these traders are usually found selling their goods in different markets.
2. Fixed Shops:
These shops are of two type’s viz. (A) Small scale and (B) Large scale.
(a)Small Scale:
There are different types of small retailers which are explained as under:
- Street stalls holders:These retailers carry their business on a very small scale basis in busy and crowded streets by erecting permanent shops. They purchase goods in large quantities from the wholesalers and local suppliers for reselling to the ultimate consumers.usually deal in household articles and products of daily need. These stall holders are usually sole proprietors of their shops i.e. carrying every activity right from buying till final disbursement of goods to the consumers.
- Second Hand Goods Sellers: These dealers deal in second hand or used articles. They purchase these articles from public or private auctions and private households. These articles usually include used garments, furniture, books etc. These dealers meet the needs of the poor people who cannot afford new articles.
- General Shops:They deal in different variety of goods and are known as general merchants. The goods are meant for daily use or household purposes. They carry their business in permanent shops. They manage the shops themselves and are most often assisted by sales assistants.Usually goods are sold on credit by these merchants to their permanent customers. They also provide free home delivery service and facility of exchange of rejected goods to the customers.
- Speciality Shops: These retailers deal in one particular line of goods e.g. books, utensils, shoes and medicines etc. These shops can be operated on small scale basis and managed by the owners themselves assisted by salesmen.The most important advantage which can be derived from these shops is that the owners possess the specialised knowledge about the product which is very helpful in satisfying the customers.
(B) Large Scale Retailers:
The second type of retailers under fixed shops is large scale retailers. The large scale production and rapid urbanisation are responsible for the establishment of large scale retailing organisations.
Features <!-- [if !supportLineBreakNewLine]--> <!--[endif]-->
- Normally run as a public limited company
- Capital needed is very large
- Large Assets where it easier to raise money from the bank or public limited company can borrow from the public in the form of debentures
- Normally buys in bulk direct from the manufacturers
- Sometimes may even have their own factories
- Stores in bulk doing away with the services from the wholesaler <!-- [if !supportLineBreakNewLine]--> <!--[endif]-->
Reasons why large retailers buy direct from Manufacturers <!-- [if !supportLineBreakNewLine]--> <!--[endif]-->
- Sufficient capital Manufactures who only sell in bulk normally do not entertain small order therefore large retailers must have large capital to enable them to buy in bulk.
- Better trade discount Buying from manufacturers means that the large retailers can get better trade discount, hence, they pay a lower price for their goods.
- Cash payment since large retailers have sufficient capital, they can afford to pay in cash. This means they can get even better terms than someone buying on credit.
- Enough resources to carry out functions normally undertaken by wholesalers; Large retailers normally have their own fleets of transport vehicles to sent goods to their various branches whenever the need arises Large retailers can afford to employ expert specialist buyer who know from experience exactly what goods customers want and who have the knowledge to buy on the best terms, locally or overseas Large retailers have their own warehouses and specialist staff to manage storing, bulk breaking, branding, stock keeping and so on to ensure that goods are not stored for an excessively long period until they are spoilt or out-of-date and that goods are not in shortage either.
- Larger turnover; The volume of turnover each month is so large that the large retailer can afford to buy in bulk It is no use buying in bulk (and hence, enjoying lower prices) if the goods are not sold quickly enough.<!--[endif]-->
Types of Large – scale retailers
A multiple shop system consists of a number of branch shops owned by a single business firm. This is an attempt on the part of the manufacturers or the wholesalers to establish a direct link with the consumers by avoiding middlemen. Some of the definitions of multiple shops are given as under:
“A multiple shop consists of a number of similar shops owned by a single business firm.” James Stephenson
“This is a system under which there is a large number of retail shops owned by the same proprietor, which are scattered over the various places of a particular city or a country and are engaged in the same line of activity.” Thomas
“Fundamentally, a chain store system is a group of retail stores of essentially the same type. Centrally owned and with some degree of centralized control of operation.”E.W. Cundiff and R.R. Still
From the above definitions, it is clear that multiple shops or chain stores operate at different localities in the city under the central ownership and control. The chain store or multiple shop organisations is nothing but the extension of retail business on large scale basis.
Characteristics of Multiple Shops:
The distinctive features of multiple shops are as under:
- Multiple shops specialize in one or two articles. The articles are sold by ail the similar shops charging uniform price.
- They operate on “cash and carry” principles and do not allow credit and free delivery services to customers. The goods are sold on cash basis.
- The main objective of the multiple shops is to establish direct contact with the consumers by eliminating middlemen.
- They operate under centralised control and are horizontally integrated.
- The layout of these shops is simple and similar.
- There are centralised purchases for all the shops which are undertaken by the head office.
- The branches of multiple shops are scattered throughout the city and also cater to the needs of the customers living at distant places.
- The products sold by multiple shops are mainly necessities or semi- necessities and do not require extensive selling efforts.
- The multiple shops lay emphasis on large and quick turnover.

Advantages of the multiple shops <!-- [if !supportLineBreakNewLine]--> <!--[endif]-->
- It can afford to sell at very competitive prices due to bulk purchases.
- It employs expert specialists in such matters as buying, publicity, shop layout and window display.
- The identical layout of branch premises, window displayed and shop fronts is to publicize the identity of the whole chain.
- Slow selling lines and surplus stocks in one area can be transferred to more promising areas.
- The multiple shops spread its risks and are very flexible. Losses sustained in one branch can be absorbed in the profits made by other branches and new branches can be opened in areas of developing prosperity to replace unprofitable outlets.
- It economizes on advertising when all branches are included in one advertisement.
Disadvantages of the multiple shops: <!-- [if !supportLineBreakNewLine]--> <!--[endif]-->
- Too much centralized control from headquarters leaves branch managers with little scope for initiative to meet local conditions.
- Lack of the personal touch between staff and customers does not help in establishing a loyal customers. <!-- [if !supportLineBreakNewLine]--> <!--[endif]-->
The Qualities of a Retailer
Explain the qualities of a retailer
Characteristics
The followings are some of the essential characteristics of a retailer:
- He is regarded as the last link in the chain of distribution.
- He purchases goods in large quantities from the wholesaler and sell in small quantity to the consumer.
- He deals in general products or a variety of merchandise.
- He develops personal contact with the consumer.
- He aims at providing maximum satisfaction to the consumer.
Modern Development in Retail Trade
Discuss the modern development in retail trade
Department Store: A department store is a retail establishment offering a wide range of consumer goods in different product categories known as "departments".

Main Features: <!-- [if !supportLineBreakNewLine]--> <!--[endif]-->
- It’s a large building divided into sections or departments, each selling one type of goods.
- Each department store is run by a general manager and each section in the department store will be handle by a manager.
- The duties of a manager including buying goods for his department, fixing the prices and employing his/her staff.
- Department stores sell a wide range of goods for the whole family where each department specialises in a particular line of goods for example clothing, foodstuffs, hardware and so on.
- Most department stores are found in the centre of a busy shopping area in a big city.
- Department stores can also afford to advertise expensively in order to attract customers.
- Department stores also provide facilities for the convenience of their customers like escalators, lifts, car parks, trolleys, etc.
- Example of department stores in Brunei are Hua Ho.<!-- [if !supportLineBreakNewLine]--><!--[endif]-->
Advantages of Department stores <!-- [if !supportLineBreakNewLine]--> <!--[endif]-->
- A department store is large and able to employ (take up) experienced and trained workers to handle the business efficiently.
- A department store is still able to sell its goods at competitive price because it buys in bulk at bigger discounts direct from the wholesalers or producers.
- It economizes on advertising when all branches are included in one advertisement.
- Trading losses in individual departments can be absorbed so long as the store as a whole continues to make a profit. <!-- [if !supportLineBreakNewLine]--> <!--[endif]-->
Disadvantages of Department stores <!-- [if !supportLineBreakNewLine]--> <!--[endif]-->
- It has a very high overhead expenses e.g. on rent, salary of workers, utilities like water and electricity bills.
- Normally departmental stores are located in the central part of the city, high rental adds to overhead cost which can eventually raise price of goods.
- There is the ever – present danger that market conditions in the neighborhood may worsen or that population shifts may lead to fewer customers.
Mail order is the buying of goods or services by mail delivery. The buyer places an order for the desired products with the merchant through some remote method such as through a telephone call or web site. Then, the products are delivered to the customer. Mail-order business, also called direct-mail marketing , method of merchandising in which the seller’s offer is made through mass mailing of a circular or catalog or through an advertisement placed in a newspaper or magazine and in which the buyer places an order by mail. Delivery of the goods may be made by freight, express, or parcel post on a cash-on-delivery basis. Retail mail-order selling was developed primarily for rural customers, but it now includes millions of customers in urban areas.
Super market is a large retail market that sells food and other household goods and that is usually operated on a self-service basis. OR is any business or company offering an unusually wide range of goods or services.
Features of supermarket
The main features of supermarket are as follows:
- Goal Oriented - The driving force behind every Company is increased sales and high profits. Most Companies draw out expected sales targets for every year. The duty lies on the sales team to not only meet these targets but go beyond them. Every sales person must be goal oriented and should work towards matching these sales figures.
- Confident - A sales person should be confident about the product he is selling as well as his own ability to successfully close a sale. Especially in the case of door to door selling, the sales person should be able to interact well with the prospective buyer, gain their trust, arouse an interest and eventually convince them to try a new product. Sales persons should be willing to handle all kinds of tense situations.
- Patient & Courteous - Convincing a prospective customer to buy a product is not an easy task. Selling is an art and requires patience. A sales person should be able to guide a customer through the entire process which begins with a prospective buyer's indifferent attitude towards a brand and ends with them placing an order. The sales person should be courteous and pleasant while taking a buyer through these stages.
- Personality-A good sales person is not afraid to talk to anyone who may have an interest in what he/she is selling. Listening and controlling the conversation by asking intelligent, thought provoking, interesting questions that are open ended and gather information is another key trait to successful selling. Also, eye contact, standing straight and smiling are important for an effective impression towards someone who is spending their hard earned money. There is a misunderstanding that a good salesperson has 'the gift of the gab' where as most trained sales people will have heard the saying 'You have one mouth and two ears, use them in that proportion'. A good sales person is a listener. They ask plenty of questions, and make notes of the answers. These notes (mental or written) help them find a suitable product or service for the potential customer. A successful sale is when the customer agrees with that solution
- Ethic-Many successful salespeople have a deep understanding of human behaviour and are able to use these skills to their advantage. They are aware that, although there is a process for successfully completing a sale, customers fall into a range of different personality types. For instance, a sales person would have to deal with a teacher in a totally different manner to how they would deal with a businessperson. This is because the two sets of people have a different outlook on life and would therefore have different qualities which would be important %
Qualities that define an effective sales person;
- Goal Oriented - The driving force behind every Company is increased sales and high profits. Most Companies draw out expected sales targets for every year. The duty lies on the sales team to not only meet these targets but go beyond them. Every sales person must be goal oriented and should work towards matching these sales figures.
- Confident - A sales person should be confident about the product he is selling as well as his own ability to successfully close a sale. Especially in the case of door to door selling, the sales person should be able to interact well with the prospective buyer, gain their trust, arouse an interest and eventually convince them to try a new product. Sales persons should be willing to handle all kinds of tense situations.
- Patient & Courteous - Convincing a prospective customer to buy a product is not an easy task. Selling is an art and requires patience. A sales person should be able to guide a customer through the entire process which begins with a prospective buyer's indifferent attitude towards a brand and ends with them placing an order. The sales person should be courteous and pleasant while taking a buyer through these stages.
PROBLEMS UNDERMINE DEVELOPMENT OF RETAIL TRADE IN TANZANIA
- Lack of capital
- Lack of business knowledge
- Poor government support
- Cash: Finding it and managing the cash flow. It’s hard to get and there is never enough. If you are a fast growth company you can rapidly outgrow your available sources, if you are an underperforming company you can’t get it. The majority of companies don’t manage it well. Overdrafts, credit cards and leasing/hire purchase are the most commonly used forms of finance. Factoring and invoice discounting, loans from friends and family and new equity are the least common sources. Commercial loans, grants and overdraft had become substantially harder to obtain for a significant minority of businesses. Most businesses experience some problems getting paid on time by their customers and with debt recovery. Good credit control helps to prevent this becoming a serious problem.
- Lack of a clear plan: most businesses don’t know how to plan. Lack of a plan worsens the cash problem by wasting cash chasing tempting diversions, and throwing money at problems. Equally important is revising your plan according to changing economic and business conditions and to ensure your survival in the recession.
- Ineffective leadership: this issue takes many forms. It is frequently in the form of depth of leadership. The founder of the company is too much hands-on and a) does not concentrate enough on his primary role as a leader rather than a manager; and b) fails to enlist support of competent managers and staff behind him or her either through recruitment or by outsourcing. This eventually causes the company to stop growing and eventually could lead to failure. Directors should always remember their core role and responsibilities.
- Sales/marketing effectiveness: This leads back to planning and leadership. Many businesses have not taken the time to decide what their USP is. They try to compete in conflicting areas, such as lowest price and highest service. One takes away money and the other ads cost. Part of the planning process for a new product should include a very clear answer to one simple question, “with all of the products and service available to my customers why should they buy from me?”.
QUIZ
- Describe the functions of retail.
- Differentiate between retailing and a retailer.
- Explain the advantages and disadvantages of supermarket. <!-- [if !supportLineBreakNewLine]--> <!--[endif]-->
- READ TOPIC 4: Wholesale Trade



No comments:
Post a Comment