
Life Skills Topic 4
EFFECTIVE COMMUNICATION SKILLS
Meaning of Effective Communication
The Meaning of Effective Communication
Explain the meaning of effective communication
Doing this involves effort from both the sender of the message and the
receiver. And it's a process that can be fraught with error, with
messages often misinterpreted by the recipient. When this isn't
detected, it can cause tremendous confusion, wasted effort and missed
opportunity.
In fact, communication is only successful when both the sender and the
receiver understand the same information as a result of the
communication.
By successfully getting your message across, you convey your thoughts
and ideas effectively. When not successful, the thoughts and ideas that
you convey do not necessarily reflect your own, causing a communications
breakdown and creating roadblocks that stand in the way of your goals –
both personally and professionally.
In a recent survey of recruiters from companies with more than 50,000
employees, communication skills were cited as the single more important
decisive factor in choosing managers. The survey, conducted by the
University of Pittsburgh's Katz Business School, points out that
communication skills, including written and oral presentations, as well
as an ability to work with others, are the main factor contributing to
job success.
In spite of the increasing importance placed on communication skills,
many individuals continue to struggle with this, unable to communicate
their thoughts and ideas effectively – whether in verbal or written
format. This inability makes it nearly impossible for them to compete
effectively in the workplace, and stands in the way of career
progression.
Process of Communication
The Communication Process
Describe the process of communication
The communication process have seven major elements of communication process are:
- sender
- ideas
- encoding
- communication channel
- receiver
- decoding
- feedback.
The picture below has summarized the communication process;
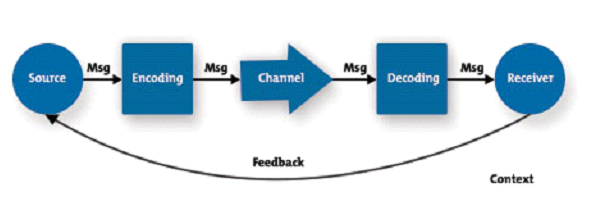
Communication barriers can pop-up at every stage of the communication
process (which consists of sender, message, channel, receiver, feedback
and context – see the diagram below) and have the potential to create
misunderstanding and confusion.
To be an effective communicator and to get your point across without
misunderstanding and confusion, your goal should be to lessen the
frequency of these barriers at each stage of this process with clear,
concise, accurate, well-planned communications. We follow the process
through below:
Source
As the source of the message, you need to be clear about why you're
communicating, and what you want to communicate. You also need to be
confident that the information you're communicating is useful and
accurate.To plan your communication :
- Understand your objective. Why are you communicating?
- Understand your audience. With whom are you communicating? What do they need to know?
- Plan what you want to say, and how you'll send the message.
- Seek feedback on how well your message was received.
When you do this, you'll be able to craft a message that will be received positively by your audience.
Good communicators use the KISS ("Keep It Simple and Straightforward")
principle. They know that less is often more, and that good
communication should be efficient as well as effective.
When you know what you want to say, decide exactly how you'll say it.
You're responsible for sending a message that's clear and concise. To
achieve this, you need to consider not only what you'll say, but also
how you think the recipient will perceive it.
We often focus on the message that we want to send, and the way in which
we'll send it. But if our message is delivered without considering the
other person's perspective, it's likely that part of that message will
be lost. To communicate more effectively:
- Understand what you truly need and want to say.
- Anticipate the other person's reaction to your message.
- Choose words and body language that allow the other person to really hear what you're saying.
Message
The message is the information that you want to communicate.
Encoding
This is the process of transferring the information you want to
communicate into a form that can be sent and correctly decoded at the
other end. Your success in encoding depends partly on your ability to
convey information clearly and simply, but also on your ability to
anticipate and eliminate sources of confusion (for example, cultural
issues, mistaken assumptions, and missing information.) A key part of
this is knowing your audience: Failure to understand who you are
communicating with will result in delivering messages that are
misunderstood.
Channel
Messages are conveyed through channels, with verbal including
face-to-face meetings, telephone and videoconferencing; and written
including letters, emails, memos, and reports.Different channels have
different strengths and weaknesses. For example, it's not particularly
effective to give a long list of directions verbally, while you'll
quickly cause problems if you criticize someone strongly by email.
Decoding
Just as successful encoding is a skill, so is successful decoding
(involving, for example, taking the time to read a message carefully, or
listen actively to it.) Just as confusion can arise from errors in
encoding, it can also arise from decoding errors. This is particularly
the case if the decoder doesn't have enough knowledge to understand the
message.
Receiver
Your message is delivered to individual members of your audience. No
doubt, you have in mind the actions or reactions you hope your message
will get from this audience. Keep in mind, though, that each of these
individuals enters into the communication process with ideas and
feelings that will undoubtedly influence their understanding of your
message, and their response. To be a successful communicator, you should
consider these before delivering your message, and act appropriately.
Feedback
Your audience will provide you with feedback, verbal and nonverbal
reactions to your communicated message. Pay close attention to this
feedback, as it is the only thing that allows you to be confident that
your audience has understood your message. If you find that there has
been a misunderstanding, at least you have the opportunity to send the
message a second time.
You need feedback, because without it, you can't be sure that people
have understood your message. Sometimes feedback is verbal, and
sometimes it's not. We've looked at the importance of asking questions
and listening carefully. However, feedback through body language is
perhaps the most important source of clues to the effectiveness of your
communication. By watching the facial expressions, gestures, and posture
of the person you're communicating with, you can spot:
- Confidence levels.
- Defensiveness.
- Agreement.
- Comprehension (or lack of understanding).
- Level of interest.
- Level of engagement with the message.
- Truthfulness (or lying/dishonesty).
As a speaker, understanding your listener's body language can give you
an opportunity to adjust your message and make it more understandable,
appealing, or interesting. As a listener, body language can show you
more about what the other person is saying. You can then ask questions
to ensure that you have, indeed, understood each other. In both
situations, you can better avoid miscommunication if it happens.
Feedback can also be formal. If you're communicating something really
important, it can often be worth asking questions of the person you're
talking to to make sure that they've understood fully. And if you're
receiving this sort of communication, repeat it in your own words to
check your understanding.
Context
The situation in which your message is delivered is the context. This
may include the surrounding environment or broader culture (corporate
culture, international cultures,and so on).
The Importance of Removing Barriers in Communication
Importance of removing the barriers in communication
Explain the importance of removing the barriers in communication
To deliver your messages effectively, you must commit to breaking down
the barriers that exist in each of these stages of the communication
process.
Let's begin with the message itself. If your message is too lengthy,
disorganized, or contains errors, you can expect the message to be
misunderstood and misinterpreted. Use of poor verbal and body language
can also confuse the message.
Barriers in context tend to stem from senders offering too much
information too fast. When in doubt here, less is oftentimes more. It is
best to be mindful of the demands on other people's time, especially in
today's ultra-busy society.
Once you understand this, you need to work to understand your audience's
culture, making sure you can converse and deliver your message to
people of different backgrounds and cultures within your own
organization, in this country and even abroad.
- READ TOPIC 5: Entrepreneurship



No comments:
Post a Comment