
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Financial Statements
General Purpose Financial Statements
Describe general purpose financial statements
Financial Statements
Definition: Financial statements are a collection of reports about an organization's financial results, financial condition, and cash flows. They are useful for the following reasons:
- To determine the ability of a business to generate cash, and the sources and uses of that cash.
- To determine whether a business has the capability to pay back its debts.
- To track financial results on a trend line to spot any looming profitability issues.
- To derive financial ratios from the statements that can indicate the condition of the business.
- To investigate the details of certain business transactions, as outlined in the disclosures that accompany the statements.
The standard contents of a set of financial statements are:
- Balance sheet. Shows the entity's assets, liabilities, and stockholders'equity as of the report date. It does not show information that covers a span of time.
- Income statement. Shows the results of the entity's operations and financial activities for the reporting period. It includes revenues, expenses, gains, and losses.
- Statement of cash flows. Shows changes in the entity's cash flows during the reporting period.
- Supplementary notes. Includes explanations of various activities, additional detail on some accounts, and other items as mandated by the applicable accounting framework, such asGAAP or IFRS.
Why General Purpose Financial Statements must follow Generally Accepted Accounting Principles
Explain why general purpose financial statements must follow generally accepted accounting principles
If a business plans to issue financial statements to outside users (such as investors or lenders), the financial statements should be formatted in accordance with one of the major accounting frameworks. These frameworks allow for some leeway in how financial statements can be structured, so statements issued by different firms even in the same industry are likely to have somewhat different appearances.
If financial statements are issued strictly for internal use, there are no guidelines, other than common usage, for how the statements are to be presented.
At the most minimal level, a business is expected to issue an income statement and balance sheet to document its monthly results and ending financial condition. The full set of financial statements is expected when a business is reporting the results for a full fiscal year, or when a publicly-held business is reporting the results of its fiscal quarters.
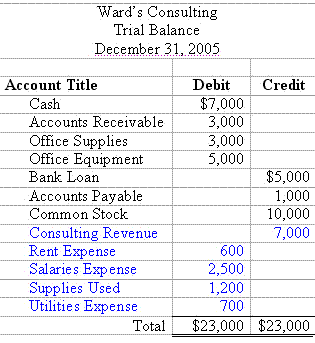
Example Trial Balance:

The trial balance ensures that the debits equal the credits.It is important to note that just because the trial balance balances, does not mean that the accounts are correct or that mistakes did not occur.There might have been transactions missed or items entered in the wrong account – for example increasing the wrong asset account when a purchase is made or the wrong expense account when a payment is made.Another potential error is that a transaction was entered twice.Nevertheless, once the trial balance is prepared and the debits and credits balance, the next step is to prepare the financial statements.
Income Statement
Describe an income statement
The income statement is prepared using the revenue and expense accounts from the trial balance.If an income statement is prepared before an entity’s year-end or before adjusting entries (discussed in future lessons) it is called an interim income statement.The income statement needs to be prepared before the balance sheet because the net income amount is needed in order to fill-out the equity section of the balance sheet.The net income relates to the increase (or in the case of a net loss, the decrease) in owner’s equity.
Preparation of a Balance Sheet
Prepare a balance sheet
Now that the net income for the period has been calculated, the balance sheet can be prepared using the asset and liability accounts and by including the net income with the other equity accounts.

When preparing balance sheets there are two formats you can use.The format above is called the Report form and the Account form lists assets on the left side and liabilities and equity on the right side.

- READ TOPIC 8: Balance Sheet (Classified)



No comments:
Post a Comment