
TOPIC 4: POLLUTION | CHEMISTRY FORM 4
“And this is my prayer: that your love may abound more and more in knowledge and depth of insight, so that you may be able to discern what is best and may be pure and blameless for the day of Christ,” –
Pollution can be defined as the introduction by human (or animal) activities, directly or indirectly, of substances or energy into the environment resulting in harmful effects which may endanger human health and harm living resources and ecosystems.
Concept of Pollution
Pollution can also be defined as the introduction of contaminants or pollutants into the natural environment. The environment comprises of living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) things such as plants, animals, air, land and water.
Humans engage in a myriad of activities such as agriculture, manufacturing, transport, waste disposal, mining etc. All of these
activities contribute to environmental pollution in one way or another.
- Terrestrial (land) pollution
- Aquatic (water) pollution
- Aerial (air) pollution
TERRESTRIAL POLLUTION
Terrestrial pollution is the degradation
or destruction of the earth‟s surface and soil, directly or indirectly,
as a result of human activities. The human activities refer to any
activities performed by man that lessens the quality and or productivity
of the land as an ideal resource for
agriculture, forestation, construction, etc.
Below are some causes of terrestrial pollution.
Agricultural activities: Because of the ever-increasing human population, demand for food has increased rapidly. Farmers often use fertilizers to increase crop production and pesticides to get rid of pests, fungi and bacteria that destroy the crops or harm animals. The overuse of such agro chemicals results in the contamination and poisoning of the soil. Other causes of soil pollution
- poor methods of irrigation which causes the leaching of cations down the soil surface;
- manure heaped on land, which may leach down the soil; and
- oil spillages that seep into the soil.
Rain: water often leaches harmful substances from the exposed mining waste into the ground. These harmful substances are like heavy metals (e.g. arsenic) and sulphuric acid or chemicals used in processing the ores (e.g. cyanide. These chemicals are another cause of soil contamination.
Deforestation and soil erosion:
carelessly leaves the land bare and hence exposes it to agents of erosion.
erosion can render a fertile land as no longer suited for agriculture, or even turn originally fertile lands into barren deserts.
Other than causing soil erosion,
deforestation has also been linked to floods which can, in turn, be seen
as another cause of land and water
pollution.
The toxins and poisonous chemicals in
the sewage gradually seep down into the ground, thus polluting the land
and killing beneficial soil
microorganisms.

Garbage disposal: Tonnes of garbage are produced each year, especially in urban and industrial areas. Garbage is collected and moved to the dumping sites allocated for that purpose.
broken down easily by the action of microorganisms,e.g. bacteria and fungi. The degradable waste matter may include materials such as rotten foods, kitchen wastes etc.
non-biodegradable wastes are such as plastic, polythene bags, metal, some clothing and glass.
Needless to say, the ability of this soil to support life is significantly affected.
Transfer of toxic wastes: Industries in developed countries produce much toxic wastes, including the deadly, reactive nuclear wastes. However, these countries have very strict laws which prohibit the dumping of such toxic wastes in their countries. The easiest and cheapest alternative is to dump them in the developing third-world countries. This is because of the greedy and selfish leaders in poor countries are easily that agree to sign contracts to allow the disposal of such dangerous wastes on their lands for their own economic gains.
HAZARDS CAUSED BY TERRESTRIAL POLLUTION
The extent of terrestrial pollution is often overlooked because its effects are not well evident to most people. However, land pollution has got a number of negative effects to soil, soil organisms, man, plants and animals. The following are some effects of terrestrial pollution:
Wastes dumped carelessly can endanger the health of man as well as other organisms. Broken glass, metal and other sharp objects may pierce one‟s skin and introduce disease germs into the body. Empty cans, glass and plastic containers are potential breeding grounds for mosquitoes which spread malaria and other diseases. Rotten organic matter may harbour many disease germs and they also produce noxious smell when they rot.
The rotten wastes also attract flies which transmit a number of enteric diseases like dysentery, cholera, diarrhoea, etc.
Land pollution causes chemical contamination to the ecosystem. This occurs when the chemicals in the waste matter poison the soil. Then plants growing on the poisoned soil, animals that eat these plants and even humans are all affected by these chemicals. This process is called biomagnifications and is a serious threat to the ecology. It can lead to the loss of some types of plants and animal life as well as create long-term health problems such as cancer and other deformities in humans. Radiation from nuclear wastes causes healthy problems such as cancers and other deformities.
Piles of waste in urban areas keep growing due to increase in waste. When this waste is burned it produces a lot of smoke
that leads to air pollution.
Soil erosion (as a form of land pollution) leads to loss of land for agriculture, settlement, forest cover, fodder patches for grazing, etc.
Land pollution leads to loss of ecosystem and hence directly or indirectly cause change in climatic patterns.
Deforestation causes imbalance in the rain cycle. A disturbed rain cycle affects a lot of factors such as reduction in the green cover. Plants help absorb excess carbon dioxide from the air and release oxygen to the atmosphere.
This process helps to balance the atmosphere. Without vegetation cover, excessive accumulation of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
causes concerns like global warming, the greenhouse effect, irregular rainfall, and floods among other imbalances.
Land pollution damages terrestrial life, especially plants. This greatly affects wildlife and other animal species which are forced to move further away and adapt to new regions or die trying to adjust.
Heaps of different wastes from mining activities make the environment unsightly and ugly.
Terrestrial pollution is a big problem in urban areas where waste production outweighs waste disposal. In such areas you find poor and blocked sewage system, effluent from domestic toilets flowing on the streets and roads, and dirty water carelessly poured on the ground. This makes life in urban areas uncomfortable and a mere nuisance.
Different Methods of Preventing Terrestrial Pollution
Recycling is the processing of changing used materials into usable raw materials instead of discarding them as wastes altogether. Scrap metals, plastic bottles and glass should be recycled instead of being dumped into the environment. Packaging materials such as plastic bags, beverage and water bottles can be recycled or re-used for packaging or carrying goods.
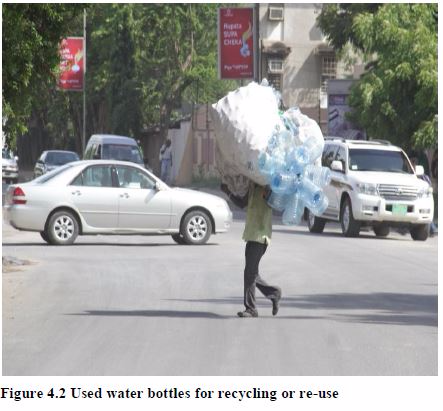

Using biodegradable materials
- biopolymers such as those used in making surgical sutures;
- photodegradable plastics, which break down upon exposure to light: and
- soluble plastics which can be broken down by water
Proper disposal of wastes
Urban waste should only be dumped in
allocated dumping sites. These sites must be far away from residential
areas to avoid the risk of spreading diseases, pest infestation and a
bad smell. The sewage should be properly treated before being drained
into dumping pools. Some of the methods that can be used to curb urban
waste problem include incineration and recycling. Paraffin should be
poured onto the sewage
pools to suffocate and kill mosquito larvae and hence prevent the spread
of malaria to residents living in the vicinity of the dumping pools.

Reducing the use of agrochemicals
chemicals pollute the soil and affect soil microorganisms a great deal.
Farmers should use organic manures and chemicals in their agricultural operations. These do not pollute the land or affect crops and animals as compared to artificial chemicals. They help to improve soil structure and hence prevent soil erosion.
The government should make and implement laws
and regulations to prevent and control terrestrial pollution. Likewise,
local government
authorities should make by-laws aiming at curbing the problem of
environmental pollution. The laws must clearly state guidelines and
procedures to be followed by everybody regarding environment sanitation.
These may include:
discharge and treatment of sewage;
disposal of lethal nuclear wastes;
use of agrochemicals in agricultural production;
use of plastic and related materials;
disposal of toxic chemicals and solid wastes from industries; and
careless littering of the environment by irresponsible people.
Creating public awareness
The general public should be educated about the importance of keeping the environment clean and the benefit of living in a clean environment. This knowledge can be conveyed through meetings or via mass media such as television, radio and newspapers. It may also be conveyed via announcements, posters and other social media.
AQUATIC POLLUTION
The Concept of Aquatic Pollution
Aquatic pollution is the introduction of
substances that lower the quality of water into water bodies such as
oceans, rivers, lakes, aquifers and ground water. This makes the water
unsafe for use in homes and industries. Water pollution also affects
living organisms (plants and
animals) living in water.
Human Activities which Cause Water Pollution
from an industrial facility discharging effluent (liquid waste) directly into a river, lake or sea.
A non-point source of water pollution is
a source that delivers pollutants into the water body indirectly
through transport or environmental change. An example of a non-point
source of water pollution is when fertilizer from a farm field is
carried into a stream
by rain (surface run off).
The following are some of the major causes of water pollution:
Many pollutants, including sewage, manure and chemical fertilizers, contain nutrients such as nitrates and phosphates. Nitrates are very soluble.
Rain washes or leaches them out of the soil into rivers. In the rivers, excess levels of nutrients (the nitrates) stimulate the growth of aquatic plants and algae. These form a layer on the water surface. A layer of these algae and aquatic plants on the surface of water will prevent light and oxygen from reaching the organisms under the water.
As a result, these organisms will begin to die. When the aquatic organisms and the algae die, bacteria feed on the remains. In the process, they use up the oxygen dissolved in the water. Thus, the amount of oxygen in water drops. As a result, fish and other river life die from oxygen starvation, and the river becomes chocked and lifeless.
This is called eutrophication. Water with limited dissolved oxygen supports only a few aquatic organisms. Such areas are called dead zones.
Oilspills in oceans and seas cause water pollution and big problems for local wildlife, fishermen and aquatic organisms. Oil spilled onto land is also carried into water bodies by surface run off. This includes drips of oil, fuel and fluid from motor vehicles, oil spilled onto the ground at filling stations; and drips of oil from industrial machinery.
These sources and many more combine together to form continual petroleum pollution to all of the world‟s waters.
Oil spilled by ships, discharge of oily wastes, and drips from motor boats are all significant sources of marine pollution. Drilling and extraction operations for oil and gas can also contaminate coastal waters and ground water.
Mining
Mining causes pollution in a number of ways. They include the following:
The mining process exposes heavy metals and sulphur compounds that were previously locked deep in the earth. Rain water leaches these compounds out of the exposed earth, resulting in “acid mine drainage” and heavy metal pollution that can continue long after the mining operations have practically ceased.
The action of rain water on piles of mining waste (tailings) transfers pollution to freshwater supplies.
In gold mining, cyanide is intentionally poured on piles of mined rock (a leach heap) to chemically extract the gold from the ore. Some of the cyanide ultimately finds its way into nearby water.
Huge pools of mining waste slurry (semi-liquid mixture) are often stored behind containment dams. If a dam leaks or bursts, water pollution is likely to take place.
Mining companies in developing countries sometimes dump mining waste directly into rivers or other water bodies as a method
of disposal.
The act of clearing the forests to get ample land for agriculture, settlement or wood leaves the land bare and exposed to the agents of denudation.
This accelerates soil erosion and the sediment is free to run into nearby streams, rivers and lakes. The increased amount of
sediment running off the land into nearby water bodies seriously affects
the fish and other aquatic life. Poor farming practices and cultivation
along and close to the rivers, exposes the soil to erosion agents. Soil
erosion causes water pollution.
Industrial processes
These substances affect the quality of water and the lives of aquatic organisms.
In developing countries about 90% of untreated sewage is discharged directly into rivers and streams. This renders the water unwholesome for domestic and other uses. Untreated sewage harbours a myriad of disease-causing organisms. This is the reason why diseases such as
contaminate ground and stream waters as well.
Marine debris is trash in the ocean. This is litter that ends up in ocean, seas or other large water bodies. The debris mainly comes from urban sewers and garbage thrown overboard from ships and boats.

Air pollution
Air pollution contributes substantially
to water pollution. Pollutants like mercury, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen
oxides, and ammonia can get into the water bodies from the air. This can
cause problems like mercury contamination in fish, acidification of
lakes and eutrophication
(nutrient pollution).
Heat
increases, the amount of oxygen that can dissolve in it also decreases.
Therefore, warm and shallow water will contain very little oxygen to an extent that the dissolved gas will not sustain aquatic life.
Many marine organisms, including mammals, sea turtles and fish, use sound to communicate, navigate and hunt. Noise from ship engines and sonars has a negative effect on these organisms. Following noise pollution, some species may find it hard to hunt or detect predators. Others may not be able to navigate properly.
The Hazards which are Caused by Water Pollution
disease-causing microorganisms are transmitted via contaminated water.
Water may be contaminated by pathogens originating from excreta. Waterborne diseases include typhoid, diarrhoea, dysentery, cholera,
bilharzia and many other diseases caused by bacteria, protozoa and viruses. Contaminated water also spread intestinal parasites such as
hook worm, round worm, and ascaris.
Algae can have direct toxic effects and finally result in oxygen deficiency in water.
tides or brown tides. Zooplankton eat the toxic algae. When fish eat the zooplankton, the toxins are passed to fish. Ultimately, when fish is
eaten by seabirds, marine mammals and man, the toxins pass to these organisms. In this way, the toxins pass to the food chain and become part of it.
Chemical pollution is caused by a number of toxic chemicals.
The oil (or chemical component of the
oil) can seep into marsh and sub-tidal sediments and remain there for
many years. This negatively
affects marsh grasses, marine worms, and other aquatic life forms that live in, on or near the sediment.
Compounds of crude oil, called the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), can remain in the marine environment for many years and are toxic to marine life at even low concentrations. Prolonged exposure to PAHs can affect development of marine organisms, increase susceptibility to disease, and distort normal reproductive cycles in many marine species.
Mercury gets into water from coal-fired power plants, gold mining and some other industrial processes. In the water, the elemental mercury is converted to methylmercury, [CH3Hg]+, by certain bacteria. Then this new form of mercury moves up the food chain of fish when small fishes are eaten by a big fish. In the end, the big fish may be eaten by man and the mercury is passed on to him.
The effects of mercury on humans are many and are already pretty well understood:
Young children and unborn babies are at a higher risk because their body systems are still developing. Exposure to mercury in unborn babies can cause neurological problems such as slower reflexes, learning deficit, delayed or incomplete mental development, autism, and brain damage.
Mercury can also cause serious nervous system problems in adults.
These problems include Parkinson‟s disease, multiple sclerosis, and
Alzheimer‟s disease. It can also cause heart disease and damage to the brain.
Industrial chemicals
Chemicals used in industrial processes
are being discharged into water bodies daily. Many chemicals can have
direct toxic effects on aquatic life.
Industrial spills into rivers kill fish for many kilometres downstream.
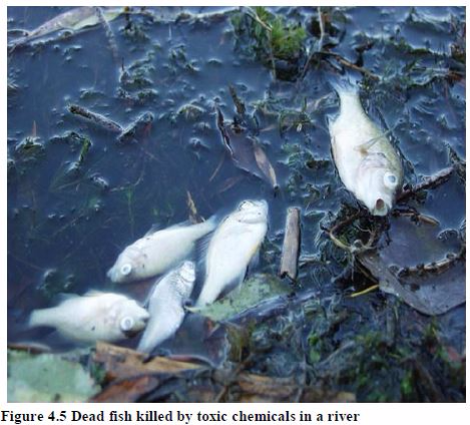

A new threat from chemicals is the
hormone-disturbing character of many chemicals. The effects of
hormone-disturbing chemicals include
interrupted sexual development, thyroid system disorders, inability to
breed, reduced immune response, and abnormal and parenting behaviour.
This refers to the out flow of acid water from metal mines or coal mines. This is how it is formed: Mining process exposes rocks and soil. When rain or surface water flows over exposed rock and soil, it combines with naturally-occurring sulphur to form sulphuric acid. The acidified water eventually finds its way to streams and ground water. This pollutes the water and affects the local aquatic life. Some streams are so acidic that they destroy the aquatic ecosystem completely.
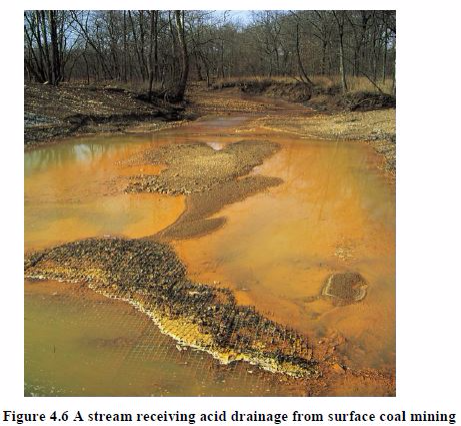

Spills and leaks:
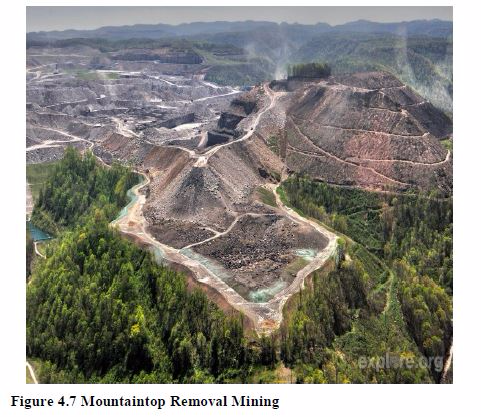
In this technique, the tops of coal-rich mountains are removed and the resulting rocks are dumped into nearby valleys. The rocks bury stream habitats altogether. This has catastrophic effect on whatever life forms that live in or around the stream.

Marine debris
problem in seas and oceans.
Marine debris can also degrade coral reefs, sea grass beds, and other aquatic habitats. This can interfere with the normal sea life.

Thermal pollution
effects of toxic chemicals. Global warming also causes extra heat to the oceans, leading to similar effects explained above.
Noise pollution from various ship
engines and sonar systems make it difficult for marine organisms like
whales, dolphins, and porpoises to
communicate, mate, find food and avoid hazards. Excessive noise
pollution may cause damage to marine animals‟ sound-sensitive organs.
This can result to internal bleeding and even death.
Ways of Preventing Water Pollution
We have seen that water pollution poses a great threat to aquatic organisms, humans and the environment. Therefore, something must be done to prevent and control this from happening.
The following are some of the methods that can be employed to prevent and control aquatic pollution:
Reducing nutrient and pesticide pollution
artificial chemicals), controlling soil erosion, and reducing or controlling the use of fertilizers and pesticides in agricultural production.
Treating sewage and industrial wastes
Sewage and industrial waste must be
treated in order to kill harmful microorganisms and detoxify poisonous
chemicals before being discharged into water bodies. This will reduce
the hazards that the chemicals and microbes contained in wastes can
cause to the environment in general.
Sewage treatment plants should be upgraded so that they can filter out
chemicals and toxins. Heated up water from industries should be cooled
down and detoxified before being release into water bodies or effluent
pools.

Forests act as a soil cover which
prevents soil erosion. They also help to absorb carbon dioxide from the
air, the excess of which causes acid
rains. Cutting down trees indescrimately exposes the soil to erosion
agents. Soil erosion produces sediments which pollute water. So the
presence of trees prevents water pollution through cutting off
deposition of sediments into water and preventing the formation of acid
rain.
Infrastructures such as buildings and industries destroy the natural shorelines which serve many purposes like fish nurseries, absorption of hurricane impacts, and filtration of the river water entering the estuary.
The government should make and enforce laws that prohibit the establishment of settlements and industries near water bodies. This will help control water pollution and its impacts to the environment.
Reducing pollution from oil spills
Enforcing the regulations and rules that govern maintenance and inspection of commercial ships and other marine vessels that leak oil and fuel into the water.
Cleaning oil spills as promptly as they occur.
Converting oil tankers into double-hull ships. A double-hull ship has two complete layers of watertight hull surface. The 178 outer layer forms the normal hull of the ship. A second inner hull forms a protective barrier to sea water in case the outer hull is damaged and leaks.
Educating the public how to keep oil out of the environment.
Controlling production of greenhouse gases
Reducing mercury emissions
However, some industries continue to use mercury on a large scale. Such industries should apply the appropriate technology to prevent mercury from being released into the environment. Where other alternatives exist, the use of mercury should be stopped completely.
The following are some of the ways through which water pollution by mines can be controlled:
- Mining companies should clean up abandoned mines which continue to release pollutants to the environment.
- New mines should not be established in areas where they are likely to cause water pollution problems.
- Mining practices which cause water pollution should be banned.
Cleaning up chemical pollution
Chemical pollution on land should be stopped. This is because chemicals on land dissolve in surface run off and finally find their way into water bodies. So preventing chemical pollution on land will automatically help keep our water clean.
AIR POLLUTION
Aerial pollution is the introduction of harmful substances into the earth‟s atmosphere.
wind erosion, pollen dispersal, and evaporation of organic compounds, hot springs, and fumaroles. However, pollution from natural occurrences does not occur very often.
Human activities that cause air
pollution include gaseous emissions from industries, burning of fossil
fuel (e.g. gas, coal), household and
agricultural chemicals, and deforestation.

The following are the chief causes of air pollution:
The act of deforestation removes trees that absorb carbon dioxide and help to reduce the level of carbon dioxide gas in the atmosphere. The
natural sources of carbon dioxide include respiration, decay, volcanic eruptions and diffusion out of the oceans.
oxygen, carbon dioxide (CO2) is produced. Other sources of carbonmonoxide include metal processing and chemical manufacturing activities, forest fires, wood burning for heat or cooking and combustion of natural gas.
presence of sunlight. It is formed in heavy traffic in hot weather, when sunlight causes the nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbons from car exhausts to react together.
Sunlight and hot weather are catalysts in the NOx/VOCs reactions that cause ground-level ozone (smog) to form. Areas with the highest concentration of motor vehicles and industrial emissions tend to have the worst ground-level ozone problems.

Nitrogen oxides
Nitrogen oxides form when fuel is burned at high temperatures, such as in automobile engines, coal-fired power plant, or any process that burns fuel. Inside car engines and power station furnaces, the air gets so hot that nitrogen and oxygen react together to form oxides of nitrogen.

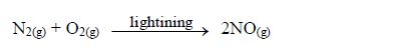
NOx and the pollutants formed from it can be transported by windover long distances. Thus, these types of pollution are notconfined to areas where they are produced, and controlling them isbest done using regional and national plans.
These are mainly particles of carbon (soot) fromburning coal in power stations and petrol in motor engines. Theother particles include smoke, nitrates, sulphates, dust particles,and organic chemicals. Exhaust fumes from leaded petrol alsocontain particles of lead.
Lead can pollute the air. Lead in air comes mainly from industrial activities like lead smelting, metal processing, lead-acid battery manufacturing, waste incineration and power generation. Lead isalso produced from combustion of airplane fuel. Leaded petrol isstill used in some developing countries. Wind-blown soil and roaddust can also contain naturally-occurring lead as well as lead fromother sources.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
Chlorofluorocarbons are organic compounds made up of carbon, chlorine and fluorine atoms.
CFCs are widely used as refrigerants in refrigerators and air condition
systems, solvents in cleaners, blowing agents in the production of foam
propellants in aerosol cans, and as fire extinguisher chemicals.
Hazards Caused by Aerial Pollution
coastlands and islands. Other effects include increase in the average temperature of the earth, change in weather patterns, and increased
desertification, which would in turn cause reduction of the arable land.
These radicals then react with the ozone molecules splitting them into oxygen atoms and free oxygen molecules. This is how the ozone layer is getting depleted.
O2(g)→4HNO3(aq)
Eutrophication
from fossil fuel air pollution adds significantly to the problem.
Eutrophication
causes algal bloom which prevents the penetration of air and light into a
water body. This deprives aquatic life of oxygen and light. When
algae die, bacteria act on them. The bacteria use dissolved oxygen in
the water, depleting the gas from the water. The depletion of oxygen in
the water (hypoxia) causes a reduction and even death of certain fish
and other aquatic organisms.

Effect on wildlife
move to new places and change their habitat. The toxic pollutants deposited in the water can also affect sea animals.
Installation of solar panels for home will help curb air pollution. This will help reduce dependency on fossil fuels, wood and charcoal which produce and emit harmful substance into the atmosphere during use. Also the use of wind energy, hydro electricity and geothermal sources of energy will greatly reduce the generation of air pollutants.

Using energy-efficient devices
Use devices that consume less electricity not only help lower electricity bills but also reduce the pollution. The domestic appliances which serve energy include energy-serving bulbs, which can be purchased from local shops.

Using public transport
Use of public mode of transport will reduce the number of motor vehicles on the road, and consequently, the emission of harmful gases by car exhaust system.

- the exhaust of new cars are fitted with catalytic converters in which harmful gases are converted to harmless ones;
- manufacturers are looking at ways to make car engines more efficient so that they can use less petrol, and other alternative fuels;
- coal is turned into smokeless fuel for use in homes; and
- scientists are looking at ways to make homes and factories more energy efficient, so that we can burn less fuel, not more.
Use of air pollution control devices
quantities.Most plants include areas for treating effluent (waste liquid) and waste gases before they are released, for example: limestone:
industry.
This is porous and has a large surface area. It is excellent at absorbing impurities. So it is used for filtering both air and liquids.
The waste gas is sprayed with water to dissolve harmful compound before they reach the chimneys. incinerators: Harmful waste gases such as solvent fumes are burned in an incinerator to give harmless products.
Ion exchangers can be designed to remove any ions you wish. electrostatic
electrodes. This method is used at cement factories to stop cement dust escaping from kilns. The trapped dust is returned to the cement store.
The National Environment Management Council (NEMC) has put in place laws and regulations that control careless pollution of the environment.
Violators of the environment sanitation laws are fined, sentenced and even stopped from operating.
Safety Measures to Protect Industrial Workers from Gaseous Pollution
The most effective way of controlling
hazards caused by chemicals is to stop using or substitute the hazardous
chemicals with the harmless ones.
Many industries are now using harmless chemicals in place of the usual
hazardous chemicals in industrial processes and operations so as to
safeguard the heath of workers.
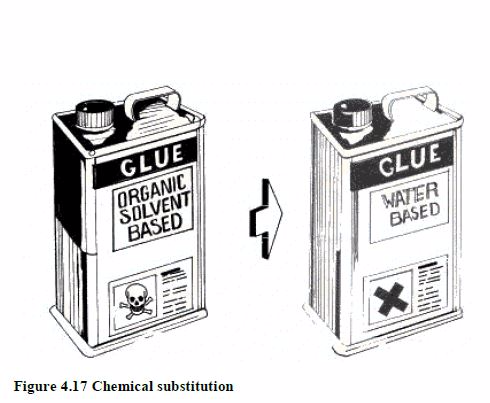
- using water-based paints or glues instead of those that are organic solvent based (figure 4.17);
- using water-detergent solutions instead of solvents; and
- using trichloromethane as a degreasing agent instead of trichloroethylene.
Workers should be provided with the necessary protective equipment and be trained on the correct use of each gear. Each worker should put on protective equipment to ensure personal safety at work place. The protective equipment include safety glasses, goggles, earmuffs and plugs, gloves, safety shoes, helmets, aprons, overalls and respirator (which covers the mouth and nose of the worker to prevent the entry of chemicals into the body by inhalation).If possible, workers must take showers at workplace before leaving work to avoid bringing chemicals at home. Dirty clothes should be left at work. If they must be washed at home, washing should be done separately, never with the family wash!

Ventilation
Ventilation means trapping the
contaminants (fumes, gases, vapours or mists) released into the air from
the process or operation and preventing them from entering the
breathing zone of the workers. The trapped contaminants are conveyed by
ducts to a collector (cyclone, filter house, scrubbers or electrostatic
precipitators) where they are removed before the air is discharged into
the outside environment. This is accomplished by a special exhaust
system or by increasing the general
ventilation.
ENVIRONMENTAL CONSERVATION
Environmental conservation is the protection and preservation of natural resources from destruction, wastage or loss. Thus, conservation of the environment involves the conservation of the natural resources. The natural resources include soil, minerals, water, air, animals and plants.
development. The following are some of the reasons why environmental conservation is crucial.
Plants and animals maintain the
ecological balance in the ecosystem. Man has been exploiting these
resources for quite a long time, to the extent that some plant and
animals species are in danger of disappearing from the earth‟s surface.
Human activities which lead to destruction of wildlife include hunting,
agriculture, settlement, mining and trade.
Environmental conservation aims at protecting plants and animals from destruction.

Economic value
The natural resources give the
environment beautiful scenery for example, flower are attractive to look
at. Forests provide shade and the air
around forest is also cold. Thus, environmental conservation initiative helps to preserve this natural beauty.

Right Attitudes, Values,and Behaviours towards Environmental Conservation
Research is being carried out on the best ways to protect and conserve the natural resources. Some of the areas of research include
- alternative sources of energy;
- methods of preventing and controlling pollution;
- sustainable use of natural resources;
- recycling and reuse of material;
- environmental impact assessment.
Pollution prevention and control
This is being done by setting up recycling factories, rehabilitating polluted areas and enacting laws and policies to control pollution,
among others.
It is crucial that everyone gets
involved in the conservation of the environment at individual level.
Each citizen should feel obliged to
take part in conserving the environment. We cannot let the task be done
by the government, agencies and the international organizations alone.
This is because we are all involved in environmental destruction, and
the effect of this destruction affects all of us.
The following are some of the ways in which you can participate in environmental conservation:
Plant more trees at home and farm fields, school and village forest. Do not cut down tress indiscrimately because doing so leaves the soil bare and vulnerable to soil erosion.
Always dump litter in areas designated for waste disposal and in litter bins. Do not just throw dirt anywhere and carelessly.
Do not start fires near forests. Farmers should not prepare their farm fields by burning the vegetation because the fire can spread and destroy trees and nearby forests. Fire also kills important soil microorganisms, thus curtailing soil fertility and productivity.
Do not harm domestic and wild animals by any means. Be kind to animals and treat them humbly.
Convey environmental conservation education to all people. Let them know the importance of conserving and living in a clean environment.
Participate in environmental conservation programmes and tasks. These include World environment Day (June 5, every year) and clear-up exercises in the local area or town.
GLOBAL WARMING
Global warming refers to an equivocal and continuing rise in the average temperature of the air and sea at the earth‟s surface. Since the early 20th century, the global air and sea surface temperature has increased by about 0.8°C, with about two-thirds of the increase occurring since 1980. Each of the last three decades has been successively warmer at the earth‟s surface than preceding decades since 1850.
The sun‟s light (also called solar radiation) passes through the atmosphere and hits the earth‟s surface. Energy from the sunlight is absorbed by the earth‟s surface in form of heat, making it warmer. Some of this heat energy (also called infrared radiation) is released back into the atmosphere. Certain gases, called greenhouse gases, form a layer in the earth‟s upper atmosphere that prevents much of this heat from leaving the atmosphere and going out into space. These gases act like the glass of a greenhouse or window: they let light in, but keep some of the heat from passing back out.
How the Major “Greenhouse” Gases are Produced
Global warming is mostly caused by increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. The greenhouse gases include water
vapour (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), dinitrogen oxide or nitrous oxide (N2O), ozone (O3) and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
They are the main causes of global warming.
Green plants absorb carbon dioxide gas from the atmosphere and use it to manufacture their food through the process of photosynthesis. Cutting down trees means that a few trees are left to absorb carbon dioxide gas from the air. This has led to the increase in the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.

Combustion of fuel
cud-chewing animals, like cattle. The emission of methane gas into the atmosphere, therefore, increases with increase in agricultural
activities. Since 1960s the amount of methane in the air has increased by 1% per year, twice as fast as the build-up of carbon dioxide.
The sources of CFCs in the atmosphere
include refrigerators, air conditioners and aerosols. CFCs are extremely
effective greenhouse
gases. One CFC molecule is about 10,000 times more effective in trapping
heat than a carbon dioxide molecule. Some of them are up to 14,000
times effective than carbon dioxide, the main greenhouse gas.
Climatic Conditions caused by Global Warming
Extreme weather events include record-breaking high or low temperatures, floods or intense storms, droughts, heat waves, hurricanes and tornadoes, etc. These are effective measures of climate change and global warming.

- higher or lower agricultural yields;
- melting of arctic ice and snowcaps. This causes landslides, flash floods and glacial lake overflow;
- extinction of some animal and plant species; and
- increase in the range of disease vectors, that is, organisms that cause diseases.
Change in world’s climate patterns
increasing temperatures will likely include changes in wind patterns, annual precipitation and seasonal temperature variations.
affected the timing of planting and harvesting activities. Sometimes the rains fall so heavily to cause floods, or too little leading to drought.
fact that will result in famine.
Small islands in the Caribbean, South Pacific, Mediterranean and Indian Ocean will be totally covered by ocean waters.
Revolution began in the early 1700s, the acidity of the oceans has increased about 25%.
and civil unrest worldwide.
The effect of global warming on human health is also expected to be serious. An increase in mosquito-borne diseases like malaria and dengue fever, as well as a rise in cases of chronic conditions like asthma, are already occurring, most likely as a direct result of global warming.
Ways of Preventing Global Warming
The effects of greenhouse gases in the
atmosphere will continue to be felt for many years. This is because
greenhouse gases remain in the
atmosphere for a very long period of time. For example, carbon dioxide
molecules can remain in the atmosphere for a period ranging between 50
and 100 years while that of a CFC molecule is approximately 110 years.
This means that global warming will continue even if the emission of greenhouse gases is reduced to very low levels.
A growing number of business leaders,
government officials and private citizens are increasingly concerned
about global warming and its
implications. Thus they are proposing steps to reverse the trend.
The following are some steps that can be taken to reduce the emission of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere:
Conserving the energy so as to reduce the use of fossil fuels which produce greenhouse gases. Such measures can be taken by using public transport to reduce the number of motor vehicles on the road and using cars that consume a little fuel.
Minimize the use of deodorants, as they contain CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons) that contributes to the ozone depletion, which in turn gives rise to most destructive effects.
Planting more trees (afforestation) and avoiding cutting down trees
(deforestation) carelessly. This is because forests play an important
role in absorbing carbon dioxide, thus reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Encourage the use of renewable sources of energy like wind, biomass, solar, and geothermal energy. The use of solar power and biomass should be installed widely. But there are a few obstacles that are delaying the use of these technologies.
Raise awareness! Educate people about global warming and its disastrous effects. Share various solutions to stop global warming. Make sure you take initiatives to help conserve the environment and encourage others to do the same.
Countries, including Tanzania, have ratified the international agreements aiming at minimizing the emission of greenhouse gases. One of those agreements is the Kyoto Protocol.


No comments:
Post a Comment