TOPIC 1: CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS
KINGDOM FUNGI
Member of the kingdom Fungi include fairly familiar organisms such
asmushrooms, toadstools and bracket fungi. There are also less obvious
but veryimportant members such as mold, which grow on bread, ripe fruits
and otherfood.
The General and Distinctive Features of the Kingdom Fungi
General features of kingdom fungi.
- Fungi are found in damp or wet places
- They have eukaryotic cells with a rigid protective wall made of chiti
- They are heterotrophs, some are saprophytic where others are parasitic
- They store food as glycogen
- They reproduce using spore
- They are non-mobile
Distinctive features of kingdom fungi
- They have chitin in their cell wall
- They have septate
THE PHYLA OF THE KINGDOM FUNGI
- Ascomycota
- Zygomycota
- Basidiomycota
Ascomycota
are also called sae fungi.
They produce spore in sae-like cell calledasei. These spores are called
ascopores. Examples of Ascomycota are bakers’yeast, cup fungi and
ringworm fungi.
Characteristics of phyla Ascomycota
- Their cell wall is not made by chitin but cetin polysaccharide component of phosphoric acid
- Have granulated cytoplasm
- Store food in form of glycogen
- Reproduce asexually by budding and sexually by means of ascospores.
Distinctive features
- Reproduce sexually by means of ascospores
(i) Reproduce sexually by means of ascospores
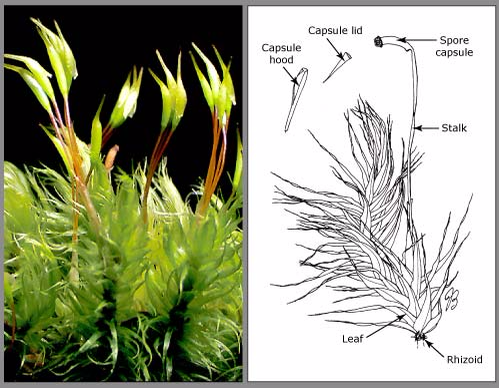
The Structure of Mosses
Mosses are small, softplants called bryophytes, that are typically
1–10 cm (0.4–4 in) tall, though some species are much larger. They
commonly grow close together in clumps or mats in damp or shady
locations. They do not have flowers or seeds, and their simple leaves
cover the thin wiry stems. At certain times mosses produce spore
capsules which may appear
as beak-like capsules borne aloft on thin stalks.
Advantage and Disadvantages of Mosses
On the advantage side, it can help to hold the bonsai soilin place and prevent it from washing out of the container.
Moss can increase the water retention capability of the soil by slowing evaporation.
On the disadvantage side, a thick carpet of moss can reduce the diffusion of gases into the soil and to the roots, which can result inroot rotorpoor drainageconditions. Moss can grow up onto the surface roots and trunk of your bonsai, and soften their bark, promoting its decay.
DIVISION FILICINOPHYTA (PTERIDOPHYTA)
General and Distinctive Features of the Division Filicinophyta
This division was formerly called Pteridophyta. The division
Filicinpphyta includes a group of primitive vascular plants. The adult
plant body in these plants is a sporophyte. It showsdifferentiation into
true roots, stems and leaves. The stem is mostly herbaceous. Leaves may
besmaller or larger. Vascular tissues are present in all the vegetative
parts of the
plant body.
Characteristics of division Filicinophytac
Members of this kingdom include horsetails, ferns and mosses.
- Reproduction involves production of spores inside special structures called sporangiawhich occur on the underside of the leaves called sporophylls. Sprangia may sometimesbe found in groups called sori.
- The plants may be homosporous – producing only one type of spore or heterosporous
-producing two different types of spores; smaller microspores and larger megaspores. - They are seedless vascular plants, which contain vascular tissues but do not produceseeds.
The Structure of Ferns
Ferns are intermediate in complexity between the more primitive
bryophytes (mosses, liverworts,and hornworts) and the more advanced seed
plants.
Like bryophytes, ferns reproduce sexually bymaking spores
rather than seeds. Most ferns produce spores on the underside or margin
of their leaves. Like seed plants, ferns have stems with a vascular
system for efficient transport of waterand food. Ferns also have leaves,
known technically as megaphylls, with a complex system ofbranched
veins.
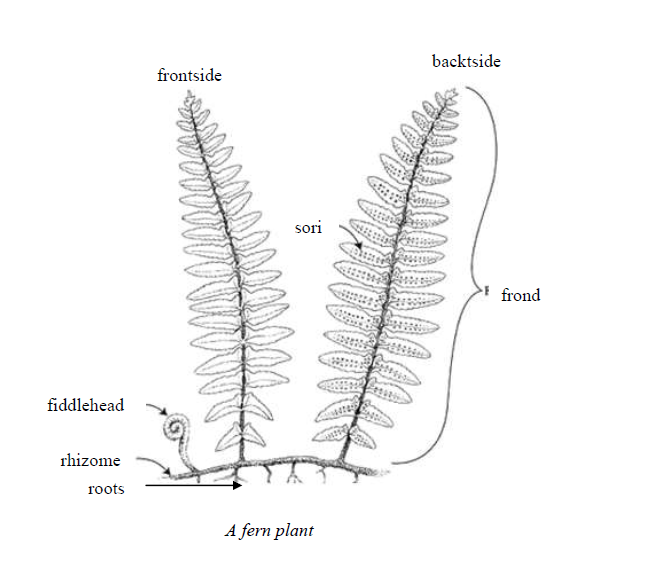
In general, ferns consist of the following structures:
Fronds. The frond is the “leaf” of a fern. It is divided into two main parts, the stipe (leaf stalk or petiole)and the blade (the leafy expanded portion of the frond).
Rhizomes. Rhizomes would be comparable to “stems” in
the flowering plants. Fronds arise from the rhizome. In some epiphytic
ferns (ferns that grow on trees) and in terrestrial creeping ferns the
rhizome roams widely and is quite visible.The rhizome contains the
conducting tissues (xylem and phloem) and the strengthening
tissues(sclerenchyma fibres). The conducting tissue, known
as the vascular bundle, carries the water,minerals, and nutrients throughout the plant.
Roots. Roots are formed from the rhizomes or
sometimes from the stipe. The roots usually do not divide once they grow
from the rhizome. Tree fern roots grow down from the crown and help
thicken and strengthen the trunk. The
roots anchor the plant to the ground and absorb water and minerals.
Sporangia. The sporangia are the reproductive structures of the ferns and fern allies.
They
produce the dustlikespores that are the “seeds” by which ferns are
propagated. Several sporangia grouped together are called a sorus. Most
ferns have their sporangia on the underside of the frond,arranged in an
organized pattern usually associated with veins in the pinnule (leaf).
Many times(but not always) the ferns provide a protective covering for
the sorus called an indusium.
Spores. The “seeds” of the ferns and fern allies are called spores. Normally they are formed in groups offour. Spores contain oil droplets and sometimes chlorophyll in their nucleus.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ferns
Advantages of ferns
- Some ferns are edible and hence serve as a source of food.
- They provide nutrients to the soil to improve soil fertility.
- They cover the soil and prevent soil erosion.
- They are used as decoration materials.
Disadvantages of ferns
- They harbour dangerous organisms like snakes and insects.
- Some ferns are poisonous when eaten.



No comments:
Post a Comment